12. Some Lessons from Capital Market History
1. Risky assets, on average, earn a risk premium. There is a reward for bearing risk
2. The greater the potential reward from a risky investment, the greater is the risk
3. the concept of market efficiency
- In an efficient market, prices adjust quickly and correctly to new information
- EHM: All investments in the market are 0 NPV
- Consequently, asset prices in efficient markets are rarely too high or too low
The form of market efficiency
- Weak form efficient
- current price of stock reflects the stock's own past prices
- Do not searching for patterns in historical prices to identifying mispriced stocks
- Semistrong form efficient
- All public information is reflected in the stock price
- There is inside information not reflected in the price of the stock
- Strong form efficient
- all information of every kind is reflected in stock prices
13. Return, Risk, and the Security Market Line

Risk premium = Expected Return - Risk free rate
Total return = Expected return + Unexpected return
+) Expected return: the information that shareholders' understanding of market today
+) Unexpected Return: news, government figures(GDP)....
Announcement = Expected part + Surprise




Why SML?
- compare (the expected return on that new investment) to (what the financial market offers on an investment with the same beta) whether or not an investment has a positive NPV
14. Options and Corporate Finance
Options are contracts giving the right, but not the obligation, to buy and sell underlying assets at a fixed price during a specified time period.



- These options give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell (the put option) or buy (the call option) shares of common stock at a given price
- 5 factors of option:
- price of the underlying asset (S): 기초자산
- exercise price (E): 행사가
- expiration date (t): 만기일
- interest rate on risk-free bonds (Rf): 무위험이자율
- volatility of the underlying asset’s value(sigma^2): 기초자산가치의 변동성 -> 위험



- 5 factors of option:
- employee stock options (ESO)
- similar to call options and serve to motivate employees to boost stock prices
- simply substitute for ordinary wages
- compensation for many workers, particularly at more senior management levels
- aligining shareholder and management interest
- always "at the money" when they issued (intrinsic value = 0)
- Not be sold during 'vesting' period
- ESO Repricing
- Underwater: the granted ESO option's stock falls significantly
- Restruck (Reprice): decide to lower strike price on underwater options
- Sadly, in that case employee may leave the company
- But a lowered strike price is a reward for failing
- similar to call options and serve to motivate employees to boost stock prices
- Almost all capital budgeting proposals can be viewed as real options
- Also, projects and operations contain implicit options
- real option: 부동산 월세집 알아볼 때 미리 내는 계약금. 이는 마치 콜옵션을 구매하는 것.
- Even if NPV is negative on today, perpetual cash flow is considered to valuable
- managerial option: Opportunities that managers can exploit if certain things happen in the future
- Contigency Planning: option to expand, the option to abandon, and the option to suspend or contract operations
- Strategic options: options for future, related business products or strategies
- The information gained for the actions are all valuable, but not reliable dollar figure
- Using the sales experience gained from the pilot, the firm can then evaluate whether or not to open more outlets
- The information gained for the actions are all valuable, but not reliable dollar figure
- real option: 부동산 월세집 알아볼 때 미리 내는 계약금. 이는 마치 콜옵션을 구매하는 것.
- Also, projects and operations contain implicit options
- A warrant(신주인수권부사채) gives the holder the right to buy shares of common stock directly from the company at a fixed exercise price for a given period of time.
- Typically, warrants are issued in a package with bonds
- unique feature: the number of shares of stock that the holder can buy
- Afterwards, they often can be detached and traded separately
- Difference between Warrants and Call options
- Call options are issued by individuals, Warrent are issued by firms
- In Call option, investor buys stock from another investor.
- In Warrents, firm must issue new shares of stock
- If warrant is exercised, the firm receives some cash and the nubmer of shares outstanding increrase
- Earnings Dilution
- Warrent and Convertible bonds cause the number of shares to increase, so earning per prices decrease (diluted EPS < basic EPS)
- Call options are issued by individuals, Warrent are issued by firms
- Typically, warrants are issued in a package with bonds
- A convertible bond: combination of a straight bond and a call option
- The holder can give up the bond in exchange for a fixed number of shares of stock
- unique feature
- (conversion ratio) The number of shares per bond received for conversion into stock
- (conversion premium) The difference between the conversion price and the current stock price, divided by the current stock price
- unique feature
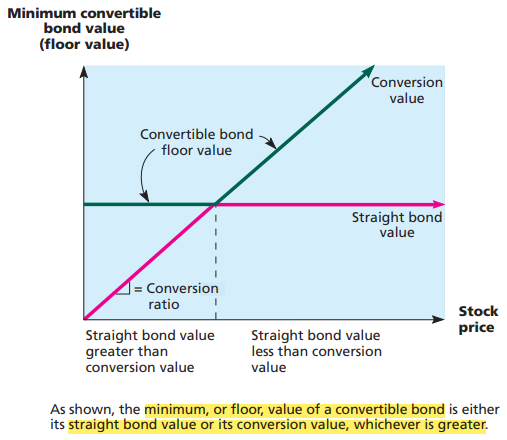
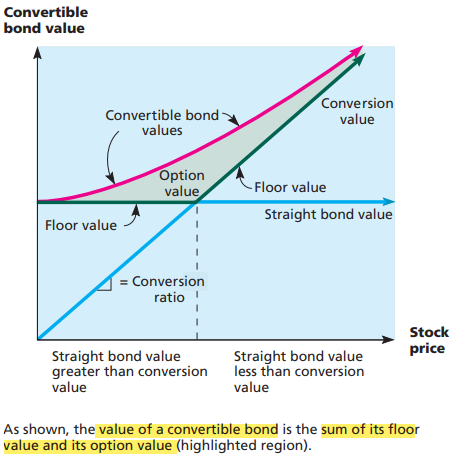
- The minimum value of a convertible bond is given by its straight bond value or its conversion value, whichever is greater
- The holder can give up the bond in exchange for a fixed number of shares of stock
- Many other corporate securities have option features
- Bonds with call provisions, bonds with put provisions, and bonds backed by a loan guarantee ...
'Buisness & Finance > Corporate Finance' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Pepsico's Financial Forecasting from 2021 and Captial Structure Decision (0) | 2024.01.18 |
|---|---|
| 6. Cost of Capital and Long-term Financial Policy (0) | 2024.01.14 |
| 4. Capital Budgeting (0) | 2024.01.14 |
| 3. Valuation of Future Cash Flows (0) | 2024.01.14 |
| 2. Financial Statements and Long-Term Financial Planning (0) | 2024.01.14 |