728x90
반응형
3. Working with Financial Statements
- Cash flow from assets = Cash flow to creditors + Cash flow to stockholders(owners)
- Sources and uses of cash
- how to trace the flow of cash through the business over the year
- - sources: a firm's activities that generate cash
- uses: application of cash
- Standardized financial statements
- differences in size make it difficult to compare financial statement
- how to form common-size and common–base period statements to make comparisons easier
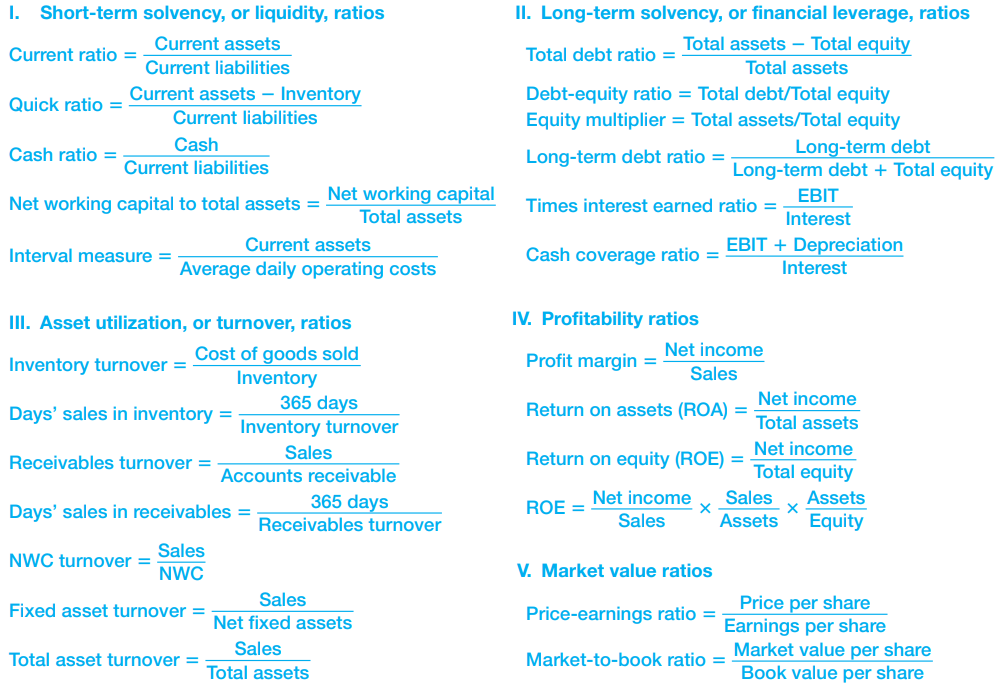
- Ratio analysis
- Evaluating ratios of accounting numbers to compare financial statement information
- Du Pont identity
- BalanceSheet
- Liquidity(유동성)
- Does inventory have Liquidity?
- Liquidity is how easily change it to cash
- Actually inventory turns back very low cash than receivables and short-term investments
- Thus, inventory may not be liquid and needs to know the quick ratio and current ratio
- Good Liquidity Ratio
- Current Ratios should be above 1
- Quick Ratios should also be above 1 or at least close to 1
- Cash Ratio depends on how liquid the receivables are, and other considerations
- To reduce liquidity, invest long-term rather than short-term and spend some cash on expenditure
- Does inventory have Liquidity?
- Solvency ~ Debt Ratio
- Solvency (Leverage) Ratios
- No negative equity
- = bankrupt
- = not have sufficient assets to pay for its liabilities
- = The company has disappeared
- The problem is Book equity (not reflect future cash flows)
- market equity = stock price X shares outstanding
- To measure leverage, use market value as equity on debt ratio
- market value of equity = Market Capitalization
- market value of assets = Market Capitalization + Total Liabilities
- Good Leverage Ratio
- below 1! No greater than 1
- if over 1, go bankrupt
- Income Statement
- Profitability Ratios
- OPAT = Operating income - tax
- OPAT != net income
- Net income = approximately (OPAT - Interest Payment)
- ROA = OPAT / Assets
- Do not use EPS to compare profitability across firms
- EPS = net income / shares outstanding changed by stock splits, share repurchases
- OPAT != net income
- EBITDA
- Operating Income (EBIT) = EBITDA - Depreciation and Amortization
- Depreciation captures implicit cost of using the company's assets to generate profits
- Thus use EBITDA-Taxes instead of OPAT
- Net profit margin = (EBITDA-Taxes) / Revenues
- ROA = (EBITDA-Taxes) / Assets
- Be careful, profitability seems larger when looking at EBITDA
- OPAT = Operating income - tax
- Profitability Ratios
- Liquidity(유동성)
- Evaluating ratios of accounting numbers to compare financial statement information

- Cash Flow Statement
- compare companies on 3 main point
- Cash from operating activities
- Cash from investing activities
- Cash from financing activities
- compare companies on 3 main point
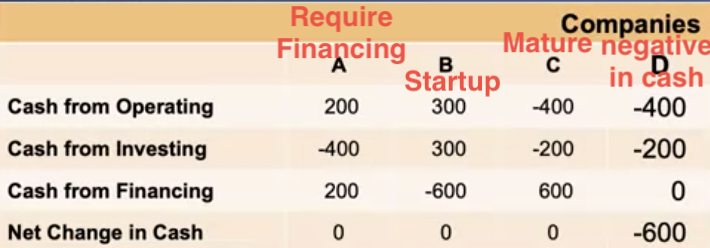
- convention on expenditure
- - when expenditure: cash out
- + when earning: cash in
- Using financial statements
- establish benchmarks for comparison purposes
- types of information that are available
- Financial Statement Analysis
- Time-trend analysis: find the possible explanations on the decline in financial statement
- Peer Group Analysis
- Peer group: ex - SIC codes
- Aspirant group: identify a set of primary competitors, not the average firm
- problem: Difficult to compare
- Do not fit any neat industry category
- Major competitors and natural peer group member in an industry may be scattered around the globe
- - Existence of difference standards, procedures, and times
+) Value over Profits
- Market value of assets / OPAT


4. Long-Term Financial Planning and Growth
- Financial planning
- it forces the firm to think about the future
- Dimension
- planning horizon: long period means the next 2~5 years
- Aggregation: process that smaller investment proposals of each firm are added up and treated as one big project
- Scenarios Division
- 1. The worst case: pessimistic assumptions
2. Normal case: the most likely assumptions
3. The best case: optimistic assumptions
- 1. The worst case: pessimistic assumptions
- what financial planning can accomplish and the components of a financial model
- Accomplishment
- Examining interactions
- explicit the ***linkages*** between investment proposals for the different operating activities of the firm and the financing choices available to the firm
- Exploring Options
- opportunity for the firm to develop, analyze, and compare many different scenarios
- Avoiding Surprises
- identify what may happen to the firm if different events take place
- Ensuring Feasibility & Internal Consistency
- Verifying that the firm's goal and plans made concerning specific areas of a firm's operations are feasible and internally consistent
- Examining interactions
- Ingredients of model
- Sales Forecast
- Pro Forma Statements
- Asset Requirements
- Financial Requirements: financing arrangements such as dividend policy and debt policy
- The Plug
- Plug variable is equity: a great number of investment opportunities & limited cash flow
- Plug variable is dividend: few growth opportunities & ample cash flow will have a surplus
- Economic Assumptions
- - level of interest rated
- firm's tax rate
- - level of interest rated
- Accomplishment
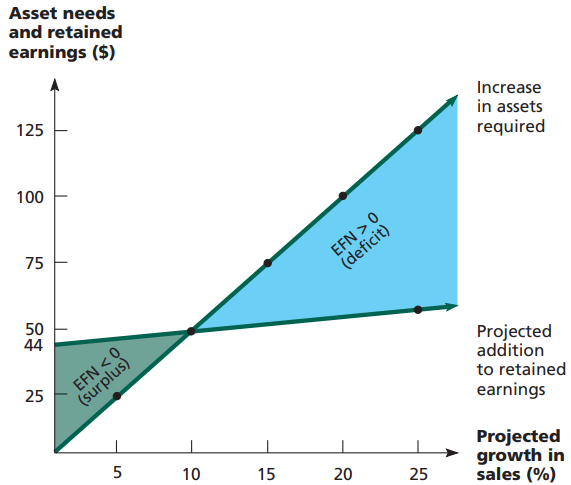
- decided by relationship between growth and financing needs
- ROE = Profit margin X total asset turnover X equity multiplier
- Therefore if a firm does not wish to sell new equity & its profit margin, dividend policy, financial policy, and total asset turnover(or capital intensity) are all fixed, then there is only one possible growth rate
- At Internal growth rate point, EFN is zero (required increase in asset = addition to retained earnings)
- EFN (external financing needed) = Total Assets - Total liabilities and equity
- the amount of financing the business requires form outside sources to remain profitable
- Sustainable growth rate: maintain growth without increasing its financial leverage
- how to increase it?
- Increase Profit Margin -> increase the firm's ability to generate funds internally
- Decrease Dividend -> increase the retention ratio & increases internally generated equity
- Rentention ratio (plowback ratio) = Addition to retained earnings / Net income
- Financial Policy: Increase in the debt-equity ratio -> increase the firm's financial leverage
- Increase Total Asset Turnover -> sales generated for each dollar in assets & decrease the firm's need for new assets as sales grow
- how to increase it?

728x90
반응형
'Buisness & Finance > Corporate Finance' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 6. Cost of Capital and Long-term Financial Policy (0) | 2024.01.14 |
|---|---|
| 5. Risk and Return (0) | 2024.01.14 |
| 4. Capital Budgeting (0) | 2024.01.14 |
| 3. Valuation of Future Cash Flows (0) | 2024.01.14 |
| 1. Overview of Corporate Finance (0) | 2024.01.14 |