728x90
반응형
Network apps 예시
< Loss-Sensitive Application>
- web
- text messaging
- remote login
- p2p file sharing
< Delay-Sensitive Application >
- multi-user network games
- voice over IP (ex-Skype)
- < Bandwidth-sensitive applications>
-
- streaming stored video ( youtube, netflix)
- real-time video conferencing
-
Creating a network application
application layer는 end system(사용자)에서만 존재하는 layer.
<종류>
- client server 구조 : HTTP, SMTP, DNS
- server
- 항상 켜져 있어야 함 ( always on )
- 고정적으로 한 개의 IP 주소만 가져야 함 (permanent IP address)
- 데이터 센터로 존재함
- client
- 항상 server와 통신 ( client끼리 절대로 X )
- 연결 여부 / 접속 여부가 달라짐
- 보통 동적 IP 주소(dynamic IP address ) - 네트워크 연결할 때마다 달라짐 (connect intermittently)
- 항상 client 가 먼저 server에게 contact
- server
- Peer-to-Peer 구조 : BitTorrent(file sharing), Internet Telephony(Skype), IPTV
- server가 항상 켜져있지 않음
- server를 위한 인프라, 대역폭 준비할 필요X
- end system끼리 직접, 임의로 통신
- peer는 서비스를 요청하면서 제공도 하는 존재
- self scalability : 새로운 peer가 등장해도 서비스를 확장시킬 필요 X
- 따로 데이터 센터 (server farm)을 구축할 필요 X
- peer들은 IP 주소가 매번 바뀌어서 관리가 복잡
- server가 항상 켜져있지 않음
Processes Communicating
process : host에서 돌아가는 program
- 같은 host라면 두 process는 OS에 의해 inter-process communication을 함
- 서로 다른 host라면 exchanging messages 로 통신
Client-server
- client process : 통신을 시작
- server process : 연결되기를 기다림
P2P
- 한 host 내에 client와 server가 동시에 존재
Sockets
- application process에서 transport layer로 data를 보내기 전 관문 같은 역할
- application layer만 app 개발자에 의해 통제되고 나머지는 모두 OS에 의해 통제된다
- transport layer로 메시지를 보내려면 socket을 이용해야 함
- 그렇게 한 단계 씩 내려가서 receiver는 아래부터 한 단계씩 올라가며 메시지를 받음
- 마지막에 socket을 통해 transport로 부터 받음

Addressing processes
messages를 받기 위해서, process는 받는 측의 식별자를 가져야 함
host는 32bit IP주소 식별
- 32bit는 충분하지 않음
- 한 host 내에서 실행되는 중 특정 process를 식별하기 위해서는 또다른 식별자가 필요
- client에 도착해서 그 안의 process 중 어느 것인지 알기 위해 port 필요
- 이것이 바로 port number
- HTTP 80 , email 25
- 식별자 = IP주소(8bit*4) + port 넘버
- IP 표기법 : dotted decimal notation
Application-layer protocol이 정의하는 것
- 메시지의 종류 ( 요청 or 응답)
- 메시지의 문법 :
- 어떤 field가 존재하고 어떻게 구분할 지 정함
- 메시지의 semantics
- 각 필드의 정보의 의미를 정함
- rule
- 언제 보내고 받을 지
- open protocol은
- RFCs로 정의되어 있음
- interoperability를 제공 - HTTP, SMTP (상호 운용성) - (기기 간 호환성 good)
- proprietary protocol (ex Skype) - 밝혀진 것이 없음
app-layer에 필요한 transport layer의 기능?
1. data integrity(loss)
- file transfer, web transactions에서는 , 100% 신뢰할만한 데이터 transfer를 보장
- audio, video처럼 , app 종류에 따라 loss를 조금 봐줄 수 있음 (tolerate)
2. timing(delay)
- Internet telephony, interactive games에서는 , low delay를 하려고 노력
3. throughput
- multimedia에서는 , 최소한의 throughput을 주려고 노력
- elastic apps(email,FTP,web transfer)에서는 , 모든 throughput을 활용
4. security

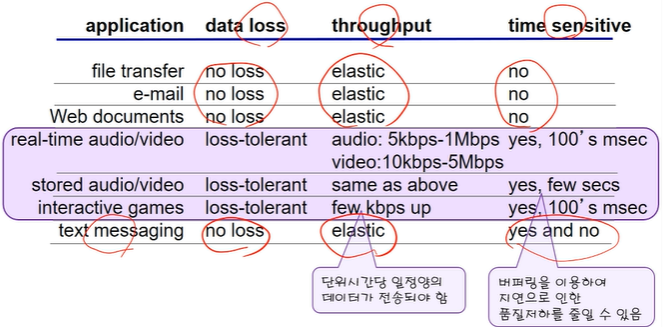
Internet transport protocols services
- 현재 인터넷에서 사용되는 transport protocol 가운데 timing, throughput guarantee, security를 지원하는 것은 없다.
TCP service
- reliable transport : loss (X)
- connection-oriented : setup 먼저
- flow control : buffer overload로 인한 loss 대비
- congestion control : 받을 수 있는 속도보다 빠르게 보내서 생긴 loss 대비
UDP service
- unreliable data transfer : loss (o)
- 제공X
- connection-oriented
- flow control, congestion control
- 그래도 이걸 사용하는 이유
- one-time transaction : 한 번만 데이터를 주고 받는 경우
- smart application : app 자체에서 이미 reliable이 확보되어서
- ex ) multimedia streaming
- reliability를 application이 스스로 구현하는 경우 application의 transport protocol로 UDP가 사용될때도 있다.

728x90
반응형
'CS > Network' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Caching (0) | 2021.10.15 |
|---|---|
| Web and HTTP ( header & cookie ) (0) | 2021.10.15 |
| Networks Under Attack : Security (0) | 2021.10.15 |
| Protocol Layers, Service Models (0) | 2021.10.15 |
| Delay, Loss, Throughput in Network (0) | 2021.10.15 |